Views: 321 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-17 Origin: Site











Aluminium extruded profiles are widely used across construction, automotive, machinery, and renewable energy industries. Their popularity comes from aluminium’s lightweight nature, strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and—most importantly—its ability to be extruded into highly customized shapes.
For engineers and buyers who work with aluminium extrusion for the first time, many technical terms and design concepts may seem confusing. This guide explains the essential knowledge you need: profile shapes, tolerances, material behavior, and commonly used terminology.
An aluminium extruded profile is a continuous cross-section shape produced by pushing heated aluminium billets through a steel die.
The final shape is determined by the die design and can be simple (angles, channels, tubes) or highly customized based on a CAD drawing.
Typical advantages include:
Consistent shapes along the entire length
Excellent precision
High design flexibility
Cost-effective mass production
Wide choice of surface finishing options
Aluminium profiles can be categorized into several general shapes:
No internal voids.
Used for frames, mechanical parts, brackets, etc.
Partially enclosed shapes with narrow openings.
Used for lighter structural applications.
Fully enclosed voids; round tubes, square tubes, multi-chamber shapes.
Used for lightweight structures, heat transfer applications, and modular systems.
To better understand the overall usage distribution of profile shapes in typical industries, the following bar chart provides a clear comparison:
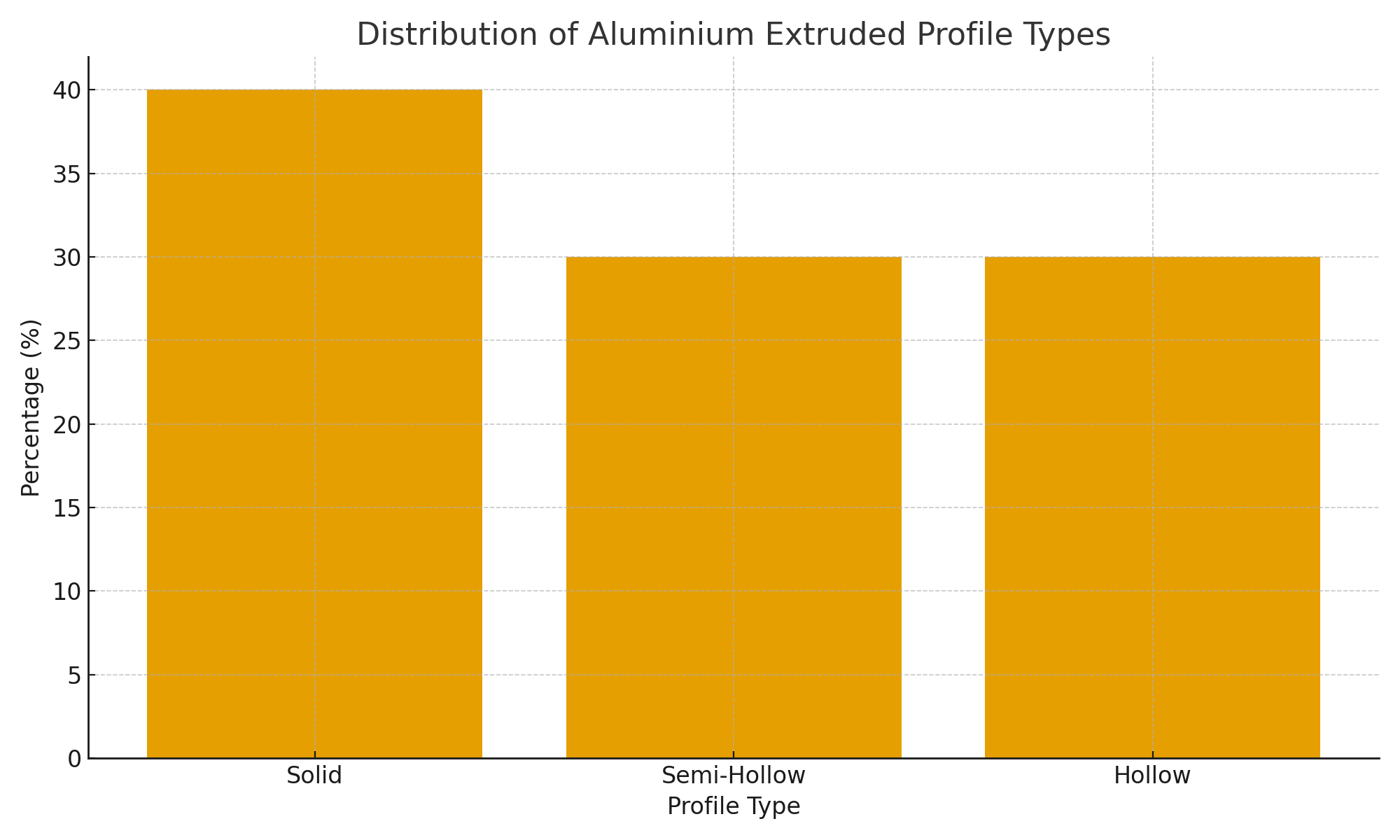
From the data above, solid profiles remain the most widely used due to their strength and simplicity, while hollow and semi-hollow profiles follow closely because of their strength-to-weight advantages.
Wall thickness directly influences:
Structural strength
Weight
Extrusion stability
Production cost
Uniform thickness and smooth transitions are recommended to improve manufacturability and control tolerance.
Tolerances define acceptable deviations in:
Dimensions
Wall thickness
Straightness
Twist
Flatness
Surface quality
Tolerances depend on shape complexity, alloy choice (6061/6063), and temper (T5/T6).
Extrusion Die — Steel tool that shapes aluminium.
Billet — Heated cylindrical aluminium block.
Alloy 6063 / 6061 — Determine hardness, corrosion resistance, machinability.
Temper T5 / T6 — Indicates mechanical strength after heat treatment.
Profile Length — Typically 3–6 meters.
Surface Finishing — Anodizing, powder coating, sandblasting, etc.
To illustrate how different aluminium alloys are selected in real projects, here is a data visualization:
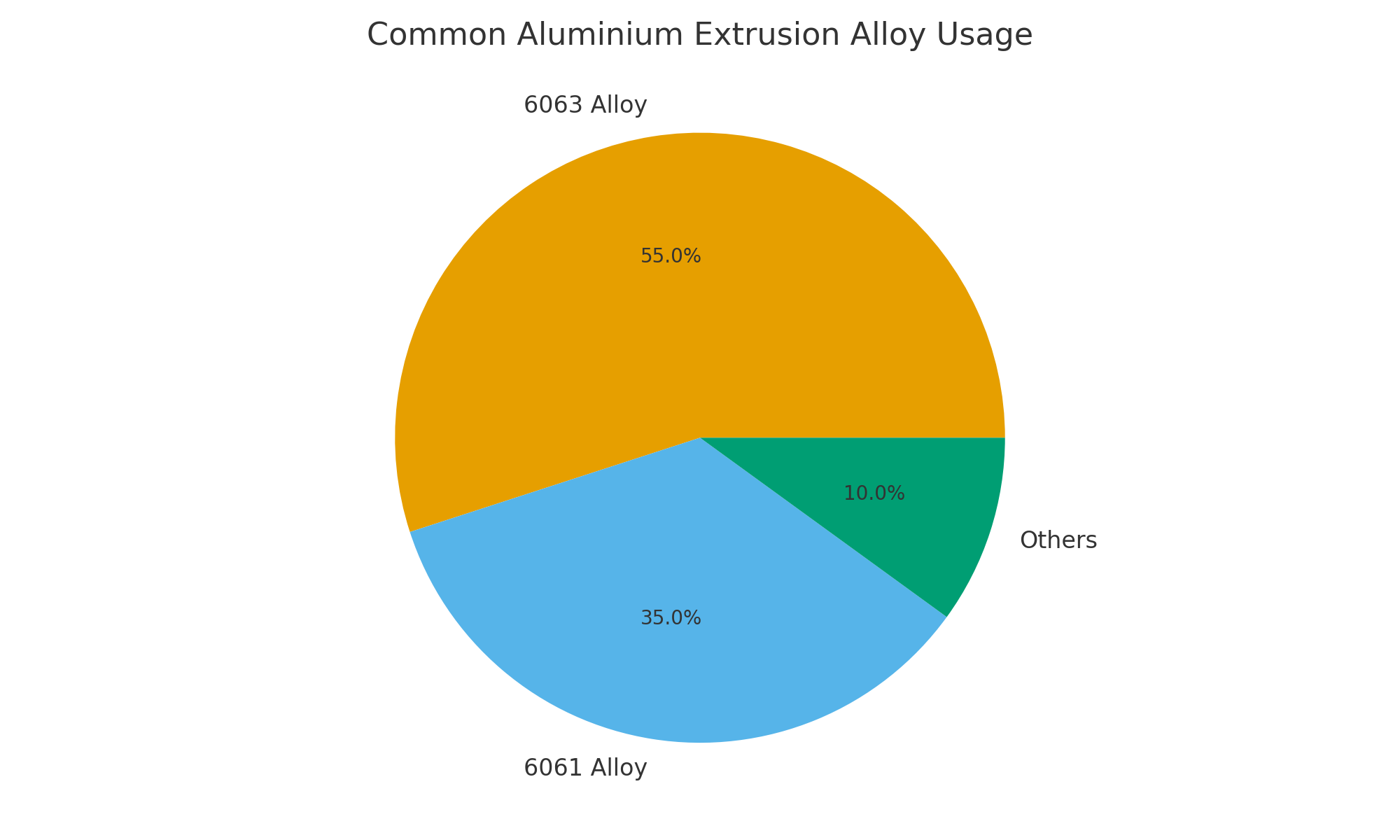
The chart demonstrates that 6063 alloy is the most commonly used due to its excellent extrudability and finishing properties, while 6061 is preferred for higher-strength applications.
The typical process:
Submit CAD drawing
Engineers evaluate the design
Die design and manufacturing
Billet heating and extrusion
Cooling and stretching
Cutting to length
Optional heat treatment and surface finishing
This workflow ensures high accuracy and stable quality.
Solar panel frames
LED light housings
Heat sinks
Automotive structures
Machine parts
Building façades
Modular rooms and charging stations
Industrial enclosures
Understanding aluminium extruded profile shapes, tolerances, material terminology, and typical alloy usage helps buyers and engineers make accurate decisions when designing custom components. With a proper CAD drawing, nearly any profile can be manufactured to meet structural, aesthetic, or functional requirements.